How to Discuss Common Questions About Climate Change
Do you want to have an educated discussion about climate change but don’t know where to begin? Read on to discover common questions and answers about climate change, including actionable ways that you can help to address this global issue.
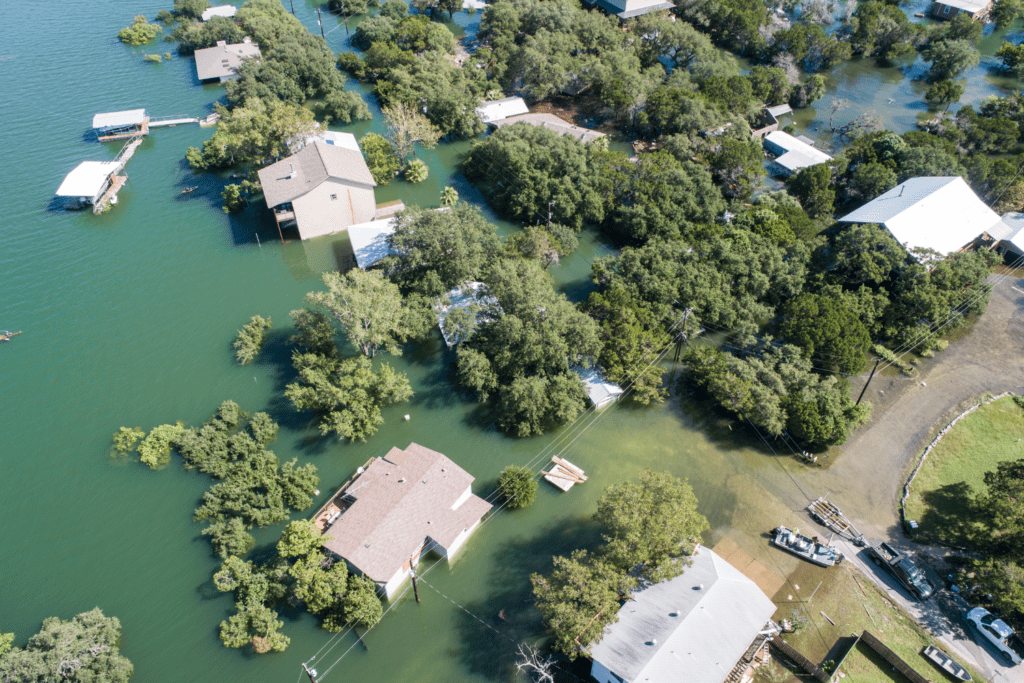

Having discussions about climate change may seem daunting. You want to make sure you understand the major concepts while remembering a host of facts and figures. Let me be the first to tell you that memorizing the details of global temperature rise or occurrences of inland flooding events and wildfires isn’t necessary. I’ve compiled a list of the most commonly asked questions, along with some helpful responses in an effort to help you have a better understanding of climate change and be able to communicate this information to anyone that’s willing to engage in conversation with you!

What is the main cause of climate change?
The main cause of climate change is the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), from human activities such as the burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) for energy, deforestation, and agriculture.
These emissions trap heat from the sun in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to an increase in global temperatures and a change in climate patterns. This phenomenon is commonly referred to as the “greenhouse effect.”
Human activities have caused the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere to increase dramatically over the past century, leading to a warming of the planet and associated impacts such as melting glaciers, rising sea levels, and more frequent and intense heat waves, droughts, and extreme weather events.
Therefore, the main cause of climate change is human activities that release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, which trap heat and alter the planet’s climate.
Are greenhouse gases good, bad or both?
The short answer is both. Greenhouse gases are atmospheric gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases, that trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere and contribute to the warming of the planet. This process is known as the greenhouse effect and is a natural phenomenon that helps regulate the planet’s temperature. Without greenhouse gases, life would not be able to exist on Earth.
However, the increased emission of greenhouse gases, primarily from human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and agriculture, has led to an unnatural enhancement of the greenhouse effect, causing global temperatures to rise and leading to climate change.
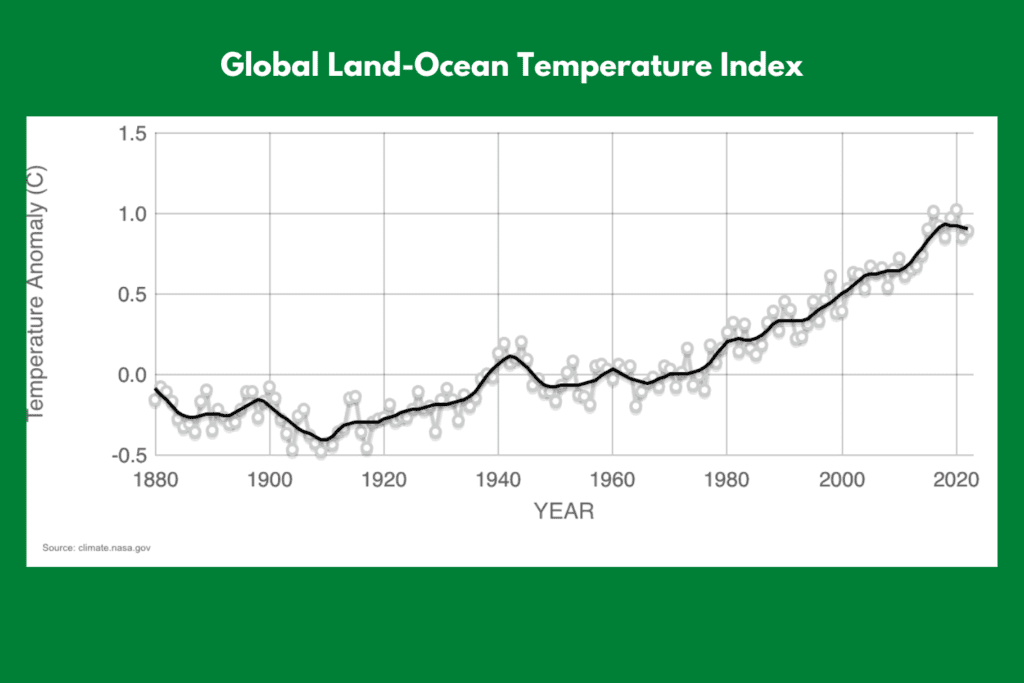
Is climate change real, and if so, how do we know?
Yes, climate change is real, and there is a broad scientific consensus that it is happening and primarily driven by human activities. This is based on extensive observational and modeling evidence, as well as decades of research by thousands of scientists across the world.
We know that the Earth’s temperature has been rising over the past century and that this warming is largely driven by the increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This is supported by a wide range of evidence, including:
- Rising global temperatures: The planet’s average surface temperature has risen about 1.8°F (1.0°C) since the late 19th century, with most of the warming occurring in the past few decades.
- Melting polar ice caps: The polar ice caps are melting, causing sea levels to rise, which can lead to coastal flooding and displacement of coastal communities.
- Changes in precipitation patterns: Climate change is causing changes in precipitation patterns, leading to more frequent droughts in some regions and increased flooding in others.
- Ocean acidification: The oceans absorb about a quarter of the carbon dioxide emissions produced by human activities, which is causing the oceans to become more acidic, with potential impacts on marine life and the food chain.
- Increased frequency of extreme weather events: Climate change is causing more frequent and intense extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, heatwaves, and droughts, which can lead to increased damage and loss of life.
- Disruptions to ecosystems: Climate change is causing disruptions to ecosystems, including changes in the distribution of plant and animal species and reductions in biodiversity.
- Agricultural impacts: Climate change is affecting agriculture, reducing crop yields and increasing the risk of food insecurity in many regions.
In addition to observational evidence, climate models have been developed and used to simulate and understand the Earth’s climate. These models have been validated by real-world observations and provide a high level of confidence in the projections of future climate change.
Overall, the scientific evidence supports the conclusion that climate change is real and primarily driven by human activities.

What are the potential consequences of climate change for human health and well-being?
Climate change can have a number of negative impacts on human health and well-being. These can include:
- Increased frequency and intensity of heatwaves, leading to heat exhaustion, dehydration, and other heat-related illnesses.
- Spread of infectious diseases through changes in the range and behavior of disease-carrying animals.
- Air pollution and increased levels of airborne allergens, leading to respiratory and cardiovascular problems.
- Water scarcity and contamination, leading to increased risk of waterborne illnesses.
- Natural disasters, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts, can displace communities and disrupt access to healthcare, food, and clean water.
- Mental health impacts, including stress, anxiety, and depression related to environmental changes and displacement.
It is important to address the impacts of climate change in order to protect human health and well-being.

What role do governments, businesses, and individuals have in addressing climate change?
Governments, businesses, and individuals each have an important role to play in addressing climate change:
- Governments have a responsibility to set policies and regulations that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and encourage the development and use of clean energy sources. This can include tax incentives for renewable energy, carbon pricing, and regulations on emissions from power plants and transportation.
- Businesses have a responsibility to minimize their own carbon footprint and to work towards sustainability. This can include investing in renewable energy, reducing waste, and promoting sustainable practices among their employees and supply chains.
- Individuals have a responsibility to make lifestyle choices that reduce their own carbon footprint. This can include reducing energy and water usage, reducing waste, eating a more plant-based diet, and supporting businesses and governments that prioritize action on climate change.
Ultimately, addressing climate change will require collective action and cooperation across all sectors of society. By working together, governments, businesses, and individuals can help ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.
While renewable energy sources are an important part of the solution to combat climate change, they are not enough on their own. A comprehensive approach that combines multiple strategies is needed to effectively address the challenges posed by climate change.
What are ways to demand sustainable climate solutions from governments and businesses?
Here are a few ways to use your individual power to demand sustainable climate solutions from governments and businesses.
- Vote with your wallet: Support companies that have a demonstrated commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility.
- Participate in advocacy and lobbying efforts: Join advocacy groups and participate in campaigns that push for sustainable policies and practices.
- Speak out: Share your views on sustainability with government representatives and business leaders. Write letters, make phone calls, and participate in public meetings to express your concerns and support for sustainability.
- Use social media: Share information about sustainability and environmental issues and encourage others to do the same.
- Support green initiatives: Advocate for and support initiatives that promote sustainability, such as renewable energy projects, sustainable transportation options, and environmental protection laws.
- Invest sustainably: Consider investing in companies and funds that prioritize environmental and social responsibility.
- Pressure through activism: Engage in peaceful protests, marches, and other forms of activism to bring attention to the importance of sustainability.
- Consume responsibly: Reduce your personal consumption of resources and adopt sustainable habits, such as conserving energy, reducing waste, and recycling.

What does the term “carbon footprint” mean?
The term “carbon footprint” refers to the total amount of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, that are emitted into the atmosphere as a result of an individual’s or organization’s activities. This includes emissions from energy consumption, transportation, food production, waste management, and other activities that are directly or indirectly linked to the production and consumption of goods and services.
A carbon footprint is usually measured in units of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) and provides a way to understand and quantify the impact of our daily activities on the environment and the climate. By calculating their carbon footprint, individuals and organizations can identify areas where they can reduce emissions and make more sustainable choices that help lower their overall impact.
The goal of reducing one’s carbon footprint is to decrease the amount of greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to global warming and climate change. This can be done through making changes to our lifestyles, such as using more energy-efficient products and reducing waste, as well as supporting policies and initiatives that promote low-carbon solutions at the national and international levels.

What are some things that individuals and families can do to lower their carbon footprint?
Individuals and families can take a variety of actions to reduce their carbon footprint and help combat climate change:
- Reduce energy use: Implement energy-saving measures, such as using energy-efficient appliances and light bulbs, and reducing unnecessary energy use.
- Use renewable energy: Consider using renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to reduce the amount of fossil fuels used for energy production.
- Reduce water usage: Conserve water by fixing leaks, taking shorter showers, and using drought-resistant plants in landscaping.
- Reduce food waste: Plan meals, buy only what is needed, and store food properly to reduce food waste. Choose locally grown and seasonal food, and reduce meat consumption, as the production of meat generates significant greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reduce transportation emissions: Use alternative transportation methods, such as public transportation, carpooling, or cycling, whenever possible, and make sure cars are well-maintained for maximum fuel efficiency.
- Purchase sustainable products: Buy products made from sustainable materials and look for products with environmentally friendly certifications, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or Energy Star.
- Support climate-friendly policies: Advocate for policies that promote renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable transportation, and support politicians and organizations working to address the climate crisis.
By taking these actions, families can lower their carbon footprint and help create a more sustainable and livable world for future generations.
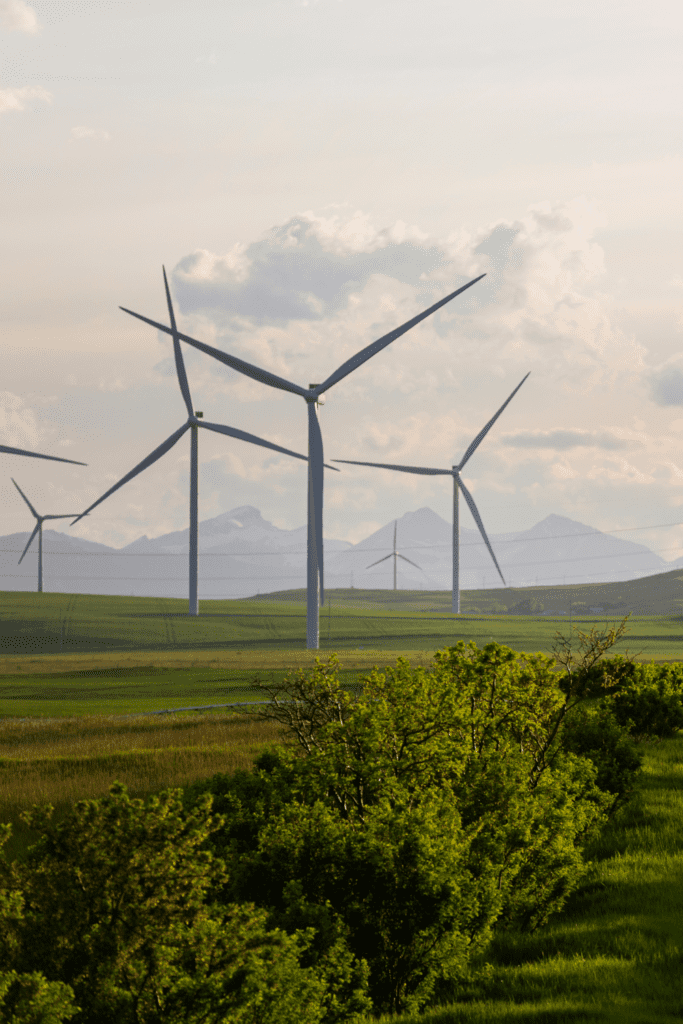


Are renewable energy sources enough to combat climate change, or do we need other solutions?
In addition to increasing the use of renewable energy, other solutions that can help address climate change include:
- Energy efficiency measures, such as improving the efficiency of buildings and appliances, can help reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Carbon capture and storage technologies can help reduce emissions from industrial processes and power generation.
- Reforestation and land-use practices that promote carbon sequestration can help remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Shifting to low-carbon transportation, such as electric vehicles and public transportation, can help reduce emissions from the transportation sector.
- Promoting sustainable agriculture practices, such as reducing fertilizer use and minimizing deforestation, can help reduce emissions from the agriculture sector.
In short, while renewable energy is a critical component of a comprehensive approach to combating climate change, it is not the only solution. A multi-faceted approach that addresses emissions from multiple sectors is needed to effectively address the challenges posed by climate change.

Can we still make a difference if we act now, or is it too late to address the issue?
It is not too late to address the issue of climate change, but time is running out. The sooner we act, the more effective our efforts will be in mitigating the impacts of climate change and preserving a livable planet for future generations.
Delaying action will only make the task more difficult and costly. Climate change is already causing devastating impacts, from sea-level rise and increased frequency of extreme weather events to the spread of infectious diseases and displacement of communities.
However, there is still time to act, and we can still make a difference. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting renewable energy, and increasing energy efficiency, we can limit the worst impacts of climate change. We must also work together, across governments, businesses, and communities, to address this global challenge.
So, while it may not be too late to address the issue of climate change, we must act now in order to ensure a sustainable future for ourselves and future generations.
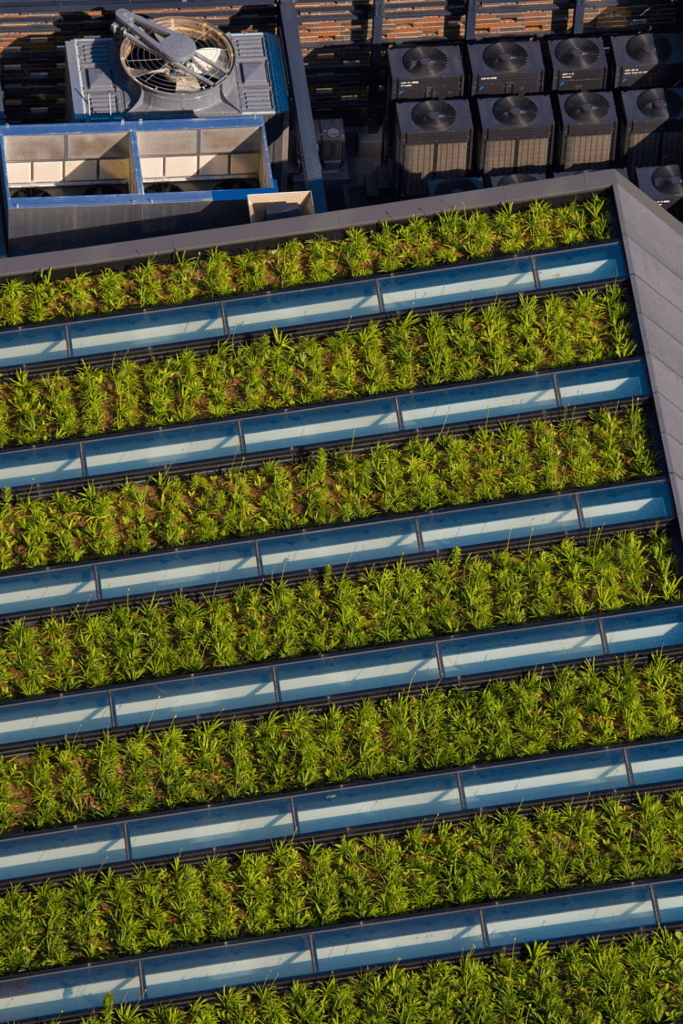

Are there any technologies or innovations that can help address climate change?
Yes, there are many technologies and innovations that can help address climate change:
- Renewable energy technologies, such as wind turbines, solar panels, and hydropower, can provide clean and abundant energy while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy efficiency technologies, such as smart building systems and energy-efficient appliances, can help reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies can capture carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes and power plants and store it underground, reducing the amount of CO2 released into the atmosphere.
- Electric vehicles (EVs) can reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector, as EVs emit far fewer pollutants than conventional vehicles and can be powered by renewable energy.
- Sustainable agriculture practices, such as precision agriculture and regenerative agriculture, can reduce emissions from the agriculture sector and increase carbon sequestration in soil.
- Green infrastructure, such as green roofs, rain gardens, and urban forests, can help reduce the urban heat island effect and promote carbon sequestration.
- Circular economy practices, such as recycling and product life extension, can reduce waste and greenhouse gas emissions.
Innovation and technological advancements will play a key role in addressing the challenges posed by climate change. By investing in these technologies and practices, we can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, adapt to the impacts of climate change, and ensure a sustainable future for ourselves and future generations.
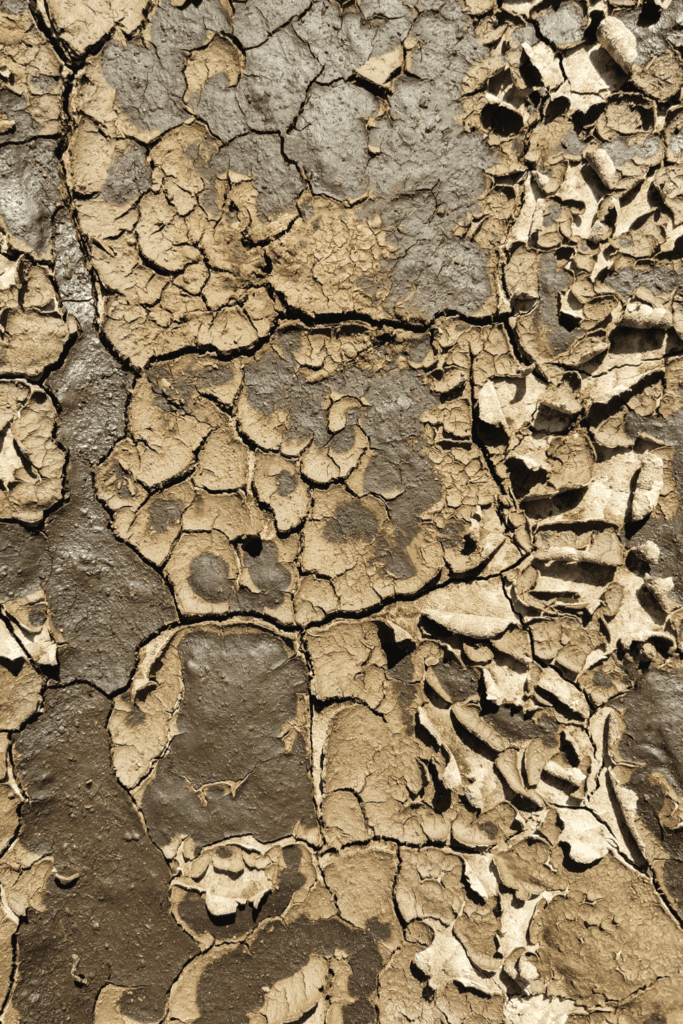
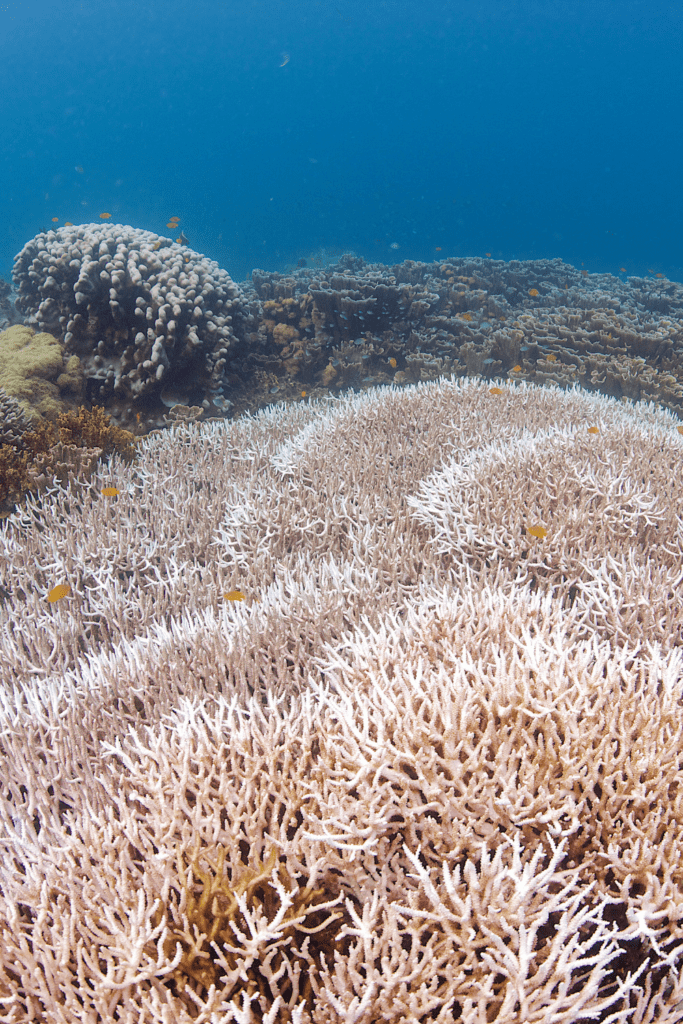


What parts of the world have seen the greatest impacts of climate change and why?
Climate change has affected different parts of the world in different ways, with some regions experiencing greater impacts than others. Some of the regions that have seen the greatest impacts include:
- Arctic and Polar regions: Warming in these regions has been faster and more pronounced than in other parts of the world, causing the melting of sea ice and glaciers, affecting wildlife, and altering local cultures.
- Small island states: Rising sea levels are a major concern for these low-lying island nations, as they face the threat of being submerged or losing their land and fresh water resources.
- Drylands: Climate change is exacerbating already arid conditions in drylands, leading to decreased agricultural productivity, increased water scarcity, and greater risk of wildfires.
- Coastal communities: Rising sea levels, coastal erosion, and more intense storms are affecting coastal communities, threatening homes and infrastructure, and exacerbating flooding and damage from storms.
- Developing countries: Developing countries are often more vulnerable to the impacts of climate change due to their limited resources and infrastructure to adapt, making it more difficult for them to respond to changes and impacts.
These impacts are occurring for a variety of reasons, including differences in geography, infrastructure, and development, as well as the natural variability in weather patterns and climates. Additionally, these regions often have large populations that rely on agriculture, fishing, and other activities that are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change.
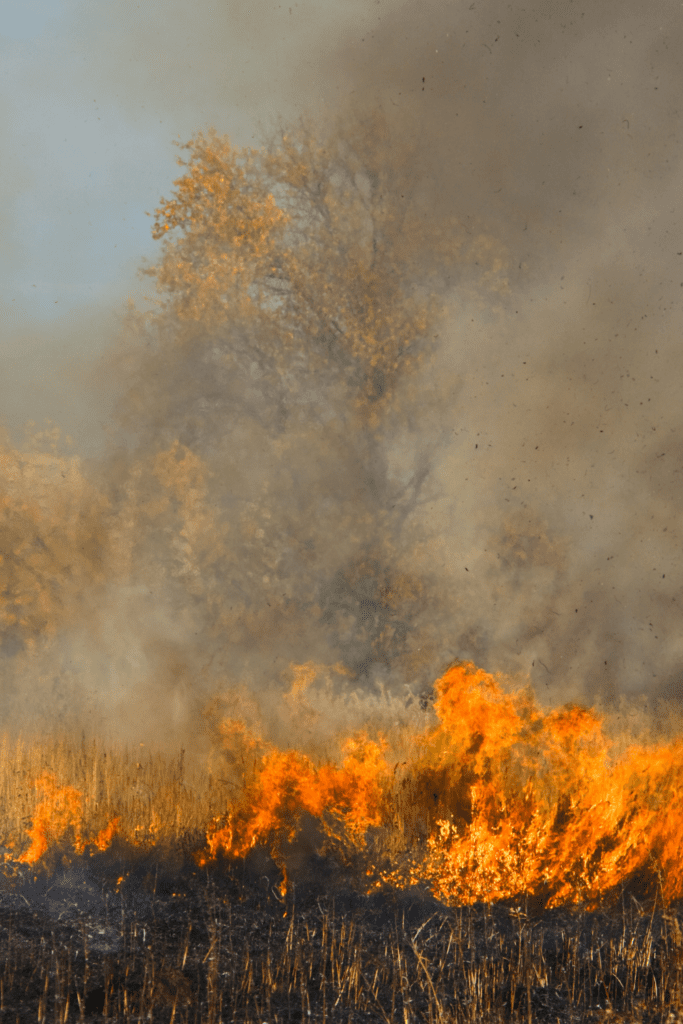

How will climate change affect future generations, and what can we do to ensure a sustainable future?
Climate change will have far-reaching and long-lasting impacts on future generations. Some of the most significant effects include:
- Rising sea levels, which can lead to increased flooding, displacement of coastal communities, and damage to infrastructure and ecosystems.
- More frequent and intense extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves, which can lead to increased damage and loss of life.
- Changes in the distribution of plant and animal species, which can lead to the loss of biodiversity and ecosystem degradation.
- Decreased access to fresh water and food, as changes in precipitation patterns and increases in temperatures can reduce crop yields and strain water resources.
- Increased health risks, as rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can lead to the spread of infectious diseases and increased air pollution.
To ensure a sustainable future, it is crucial that we take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote renewable energy, and increase energy efficiency. We must also work together, across governments, businesses, and communities, to address this global challenge.
In addition, we must invest in adaptation measures that help communities and ecosystems adapt to the impacts of climate change. This can include building more resilient infrastructure, protecting coastal areas, and promoting sustainable land-use practices.
Finally, we must work to protect the natural systems and ecosystems that support life on our planet. This includes reducing deforestation, protecting wetlands and other ecosystems, and reducing waste and pollution.
By taking these steps, we can help ensure a sustainable future for future generations and preserve a livable planet for generations to come.